[EH Wk 4] Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
Vulnerability
- A weakness in an asset that can be exploited
- Common reasons of include hardware/software misconfigurations, insecure design, inherent technology weaknesses (E.g. HTTP, FTP) and end users’ carelessness.
Vulnerability Research
- Analysis of services, and configurations to discover vulnerabilities in a system.
- Classified based on security level (low, mid, high) and exploit range (local, remote)
- Purpose is to gather information on security trends, discover weaknesses to prevent attacks, and to know how recover from one.
- Tools include databases like cwe.mitre.org, cve.mitre.org and nvd.nist.gov
Vulnerability Assessment
- In-depth examination of the ability of a system to withstand the exploitation.
- Purpose is to identify weaknesses and predict the effectiveness of security measures in protecting resources from attacks.
- Gathers information on network vulnerabilities, application and services’ vulnerabilities and configuration errors.
- Types include:
- Active Assessment – Network scanning (hosts, services, vulnerabilities)
- Passive Assessment – Network sniffing (discover active systems)
- Host-based Assessment – Configuration-level check (directories, file systems)
- More in the slides.
- Tools include OpenVAS and Nikto
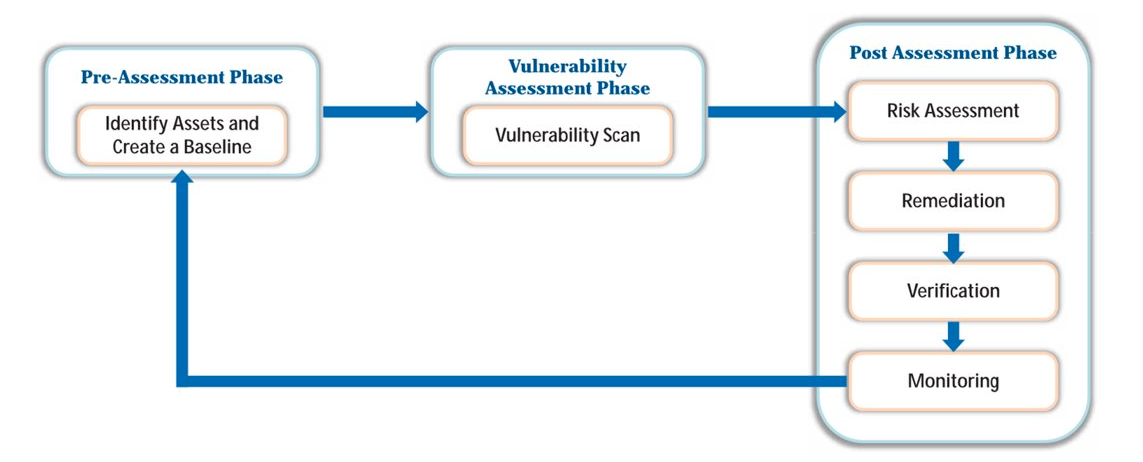
Vulnerability Management Life Cycle
- Pre-Assessment:
- Define scope, identify and prioritise assets (business processes, network architecture, etc.)
- Vulnerability Assessment:
- Run vulnerability scans, classify vulnerabilities, and assess the risk.
- Post-Assessment:
- Risk assessment (categorisation), remediation (patches), verification (rescan and check for fix), and monitoring ( periodic scans, implement procedures like IDS/IPS)
Common Vulnerability Types
- Misconfigurations: Most common vulnerability; caused by human error. E.g. open ports
- Legacy Platforms: Obsolete code; unsupported for patches.
- System Sprawl: Increased number of system/server connections without proper documentations/maintenance.
Vulnerability Assessment Reports
- Discloses risks detected, alerting organisation of possible attacks and countermeasures to fix security flaws
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.