[NS Wk 3] Security Policy and NAT Policy
Security Policy
Concepts and Operations
- Security Policy
- Rules that control network traffic by allowing or denying sessions based on traffic attributes (e.g.: Source and Destination Zone)
Operations
- Evaluated top-down; once a match is found, further rules are not evaluated
- Policies are unidirectional and requires separate rules for traffic in each direction
Sessions and Flows
- Sessions
- A connection between two devices; each session is matched to a security policy rule. Each packet is matched to a session.
Flows
- Single Flow: Multicast traffic (from one source to multiple destinations)
- Two Flows: Unicast traffic / TCP traffic (from one source to one destination)
Security Policy Rule Types and Attributes
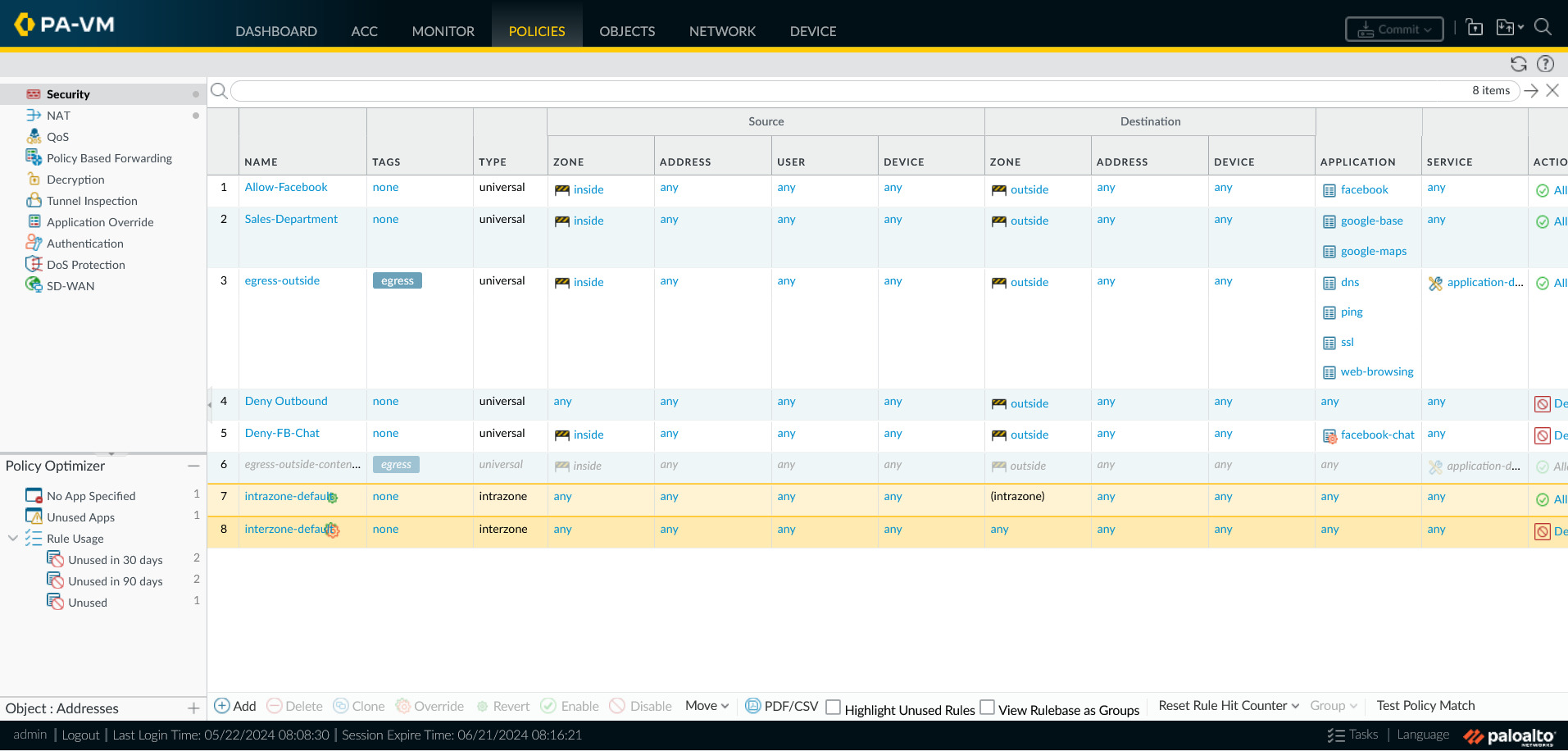
View Security Policies:
POLICIES > Security
Rule Types
- Specifies if a rule applies to traffic within a zone, between zones, or both.
- Intrazone: Traffic within a zone
- Interzone: Traffic between zones
- Universal: Traffic within and between zones
Custom vs Predefined Rules
- Custom Rules
- User-defined rules by administrators to meet specific requirements of organisation
- (+) Greater flexibility and granular control over firewall’s behaviour
- By default, all traffic is logged
- Predefined Rules
- Default security rules pre-configured with PAN firewall. Provides basic security functionality.
- (-) Cannot be modified or deleted, but can be disabled or enabled
- By default, traffic is not logged
Rule Hit Count
- Tracks how often a rule is matched
- Useful for identifying rules that are not being used
- Determines first and last usage timestamps
- Helpful in verifying configuration changes!
Rule Shadowing
- When a rule is shadowed, it is not evaluated as a rule with higher priority has already matched the traffic
- To resolve: Reorder or refine rules
Security Policy Rule Configuration
Configuration Steps
1. Add New Rule
Add new rule: POLICIES > Security > Add Rule
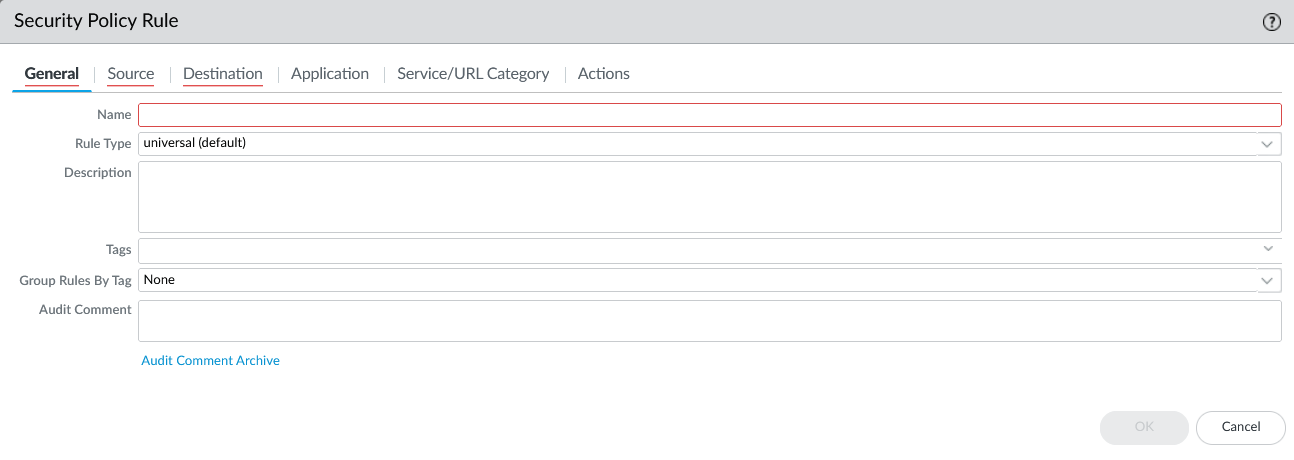
2. Source Tab
- Source Zone: Zone from which traffic originates (inside for internal traffic, outside for external traffic)
- Source Address: IP address/Region which traffic originates from (Default: Tick
Any) - Source User: User who is sending the traffic (Default: Tick
Any) - Source Device: Device from which traffic originates (Default:
Any)
3. Destination Tab
- Destination Zone: Zone to which traffic is destined (inside/outside)
- Destination Address: IP address which traffic is destined to (Default: Tick
Any) - Destination Device: Device to which traffic is destined (Default:
Any)
4. Application Tab
- Application: Application that is being used to send traffic
Anyfor services that are not application-specific (E.g. deny all traffic)- Specify application for application-specific services (E.g. facebook)
5. Service/URL Category Tab
- Service: Port number or service that is being used to send traffic (Default:
Anyfor services and URL)
6. Actions Tab
- Action: Allow/Deny traffic
- Log Setting: Session End (or Start for troubleshooting)
The default Intrazone and Interzone rules can be modified to be logged for troubleshooting by selecting the rule and clicking
Override.
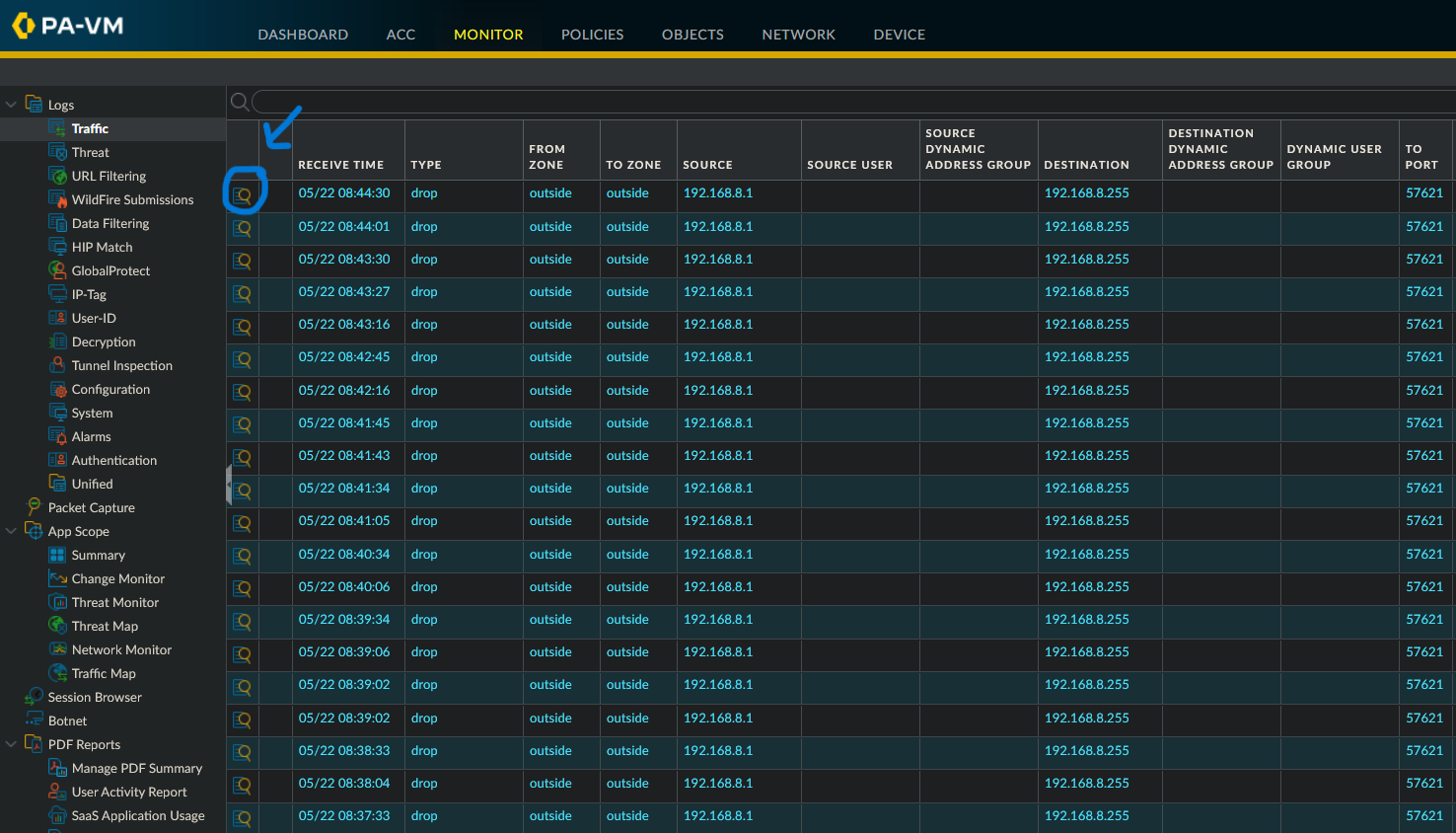
Log Monitoring
Monitor > Logs > Traffic- To view more details, click on the log entry (circled button)
NAT Policy
- Used to translate IP addresses and ports to allow traffic to flow between different networks.
- Two types: Source NAT (SNAT) and Destination NAT (DNAT)
Source NAT (SNAT)
- For private users to access public internet (outbound traffic)
- Translates internal IP addresses to external public IP addresses
- Types:
- Static IP: 1-1 fixed mapping; same internal IP always maps to same external IP with same port
- Dynamic IP: 1-1 mapping of internal to external IP from a pool of public IPs; no port number translation
- Dynamic IP and Port (DIPP): Multiple clients to 1 public IP with different source port numbers. Fewer public IPs needed.
Configurations
POLICIES > NAT > Add
| Tab | Field | Setting |
|---|---|---|
| General Tab | Name | Source NAT |
| Original Packet | Source Zone | Inside |
| Destination Zone | Outside | |
| Destination Interface | Pick internal IP address interface (e.g. ethernet1/1) | |
| Translated Packet (Source Addr Translation) |
Translation Type | Dynamic IP and Port |
| Address Type | Interface Address | |
| Interface | Pick same interface as Destination Interface | |
| Translated Address | Select IP of the interface from dropdown list |
To enable Bidirectional SNAT, enable Bi-directional under the
Translated Packet (Source Addr Translation)tab. Note: Only for static NAT.
Destination NAT (DNAT)
- For public users to access private servers (inbound traffic)
- Translates external IP addresses to internal IP addresses
- Configurations:
- Static IP: 1-1 fixed translation without port number translation
- Port Translation: Used when the destination server listens on a non-standard port.
Configurations
POLICIES > NAT > Add- Similar to SNAT, but with different settings
| Tab | Field | Setting |
|---|---|---|
| General Tab | Name | Destination NAT |
| Original Packet | Source Zone | Outside |
| Destination Zone | Inside | |
| Destination Address | Public IP | |
| Translated Packet (Destination Addr Translation) |
Translation Type | Static IP |
| Translated Address | Internal IP | |
| Translated Port | Internal Port |
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.