[NS Wk 2] Network Segmentation and Security Zones
Network Segmentation
- Network Segmentation
- Dividing a network into multiple areas (zones), each protected by a firewall with specific security policies.
- Purpose: Prevents lateral movement of attackers within the network, i.e. prevent them from gaining access to key resources if they compromise one network segment.
- Underlying principles:
- Least Privilege: Identify who needs access to what resources and grant only necessary permissions.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure compliance with industry regulations, like for credit card data (PCI DSS).
Network Interfaces and Security Zones
Network Interfaces
- Network Interfaces
- Physical or virtual ports on a device that connect to a network.
- Each interface is assigned to a single zone.
- Controlled by data plane.
Security Zones
- Security Zones
- Isolated groups of devices/users with similar security requirements.
- When used with network segmentation, reduces attack surface.
- Policy Configuration: Create Security policy rules to control interzone traffic (e.g., allow specific users or groups access to specific zones).
Interface and Zone Types
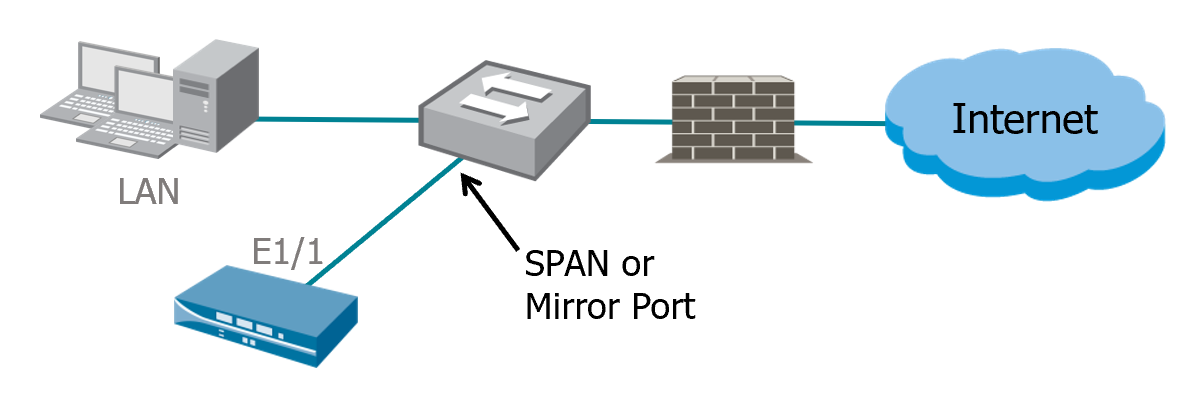
Tap Zone
- Tap Interface: Passive traffic monitoring and analysis from switch’s SPAN port or a mirror port; used for evaluation of existing networks
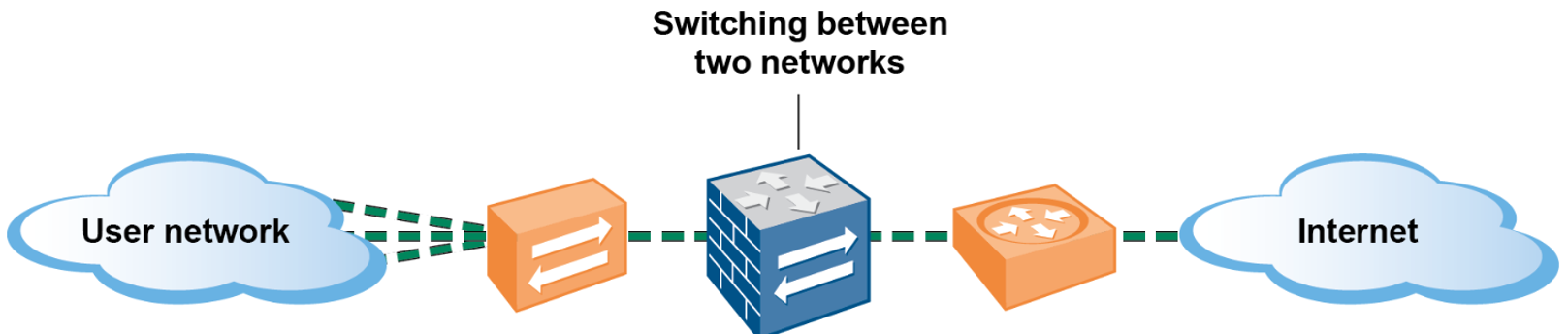
Layer 2 Zone
- Layer 2 interface: Handles traffic at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer), e.g., Ethernet frames.
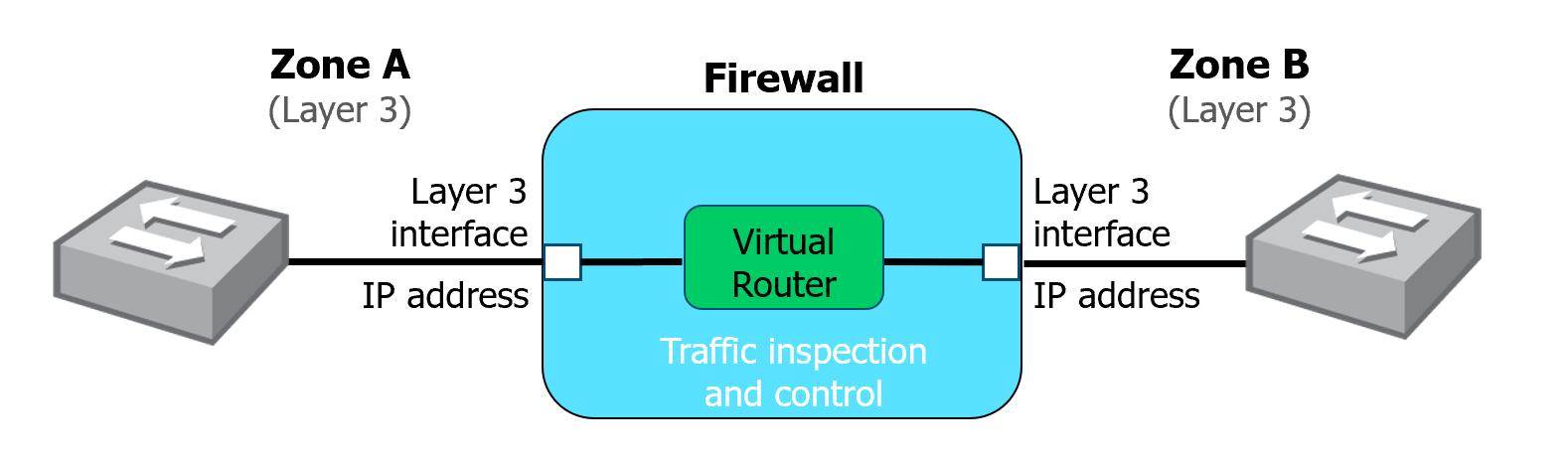
Layer 3 Zone
- Layer 3 interface: Handles traffic at Layer 3 (Network Layer), e.g., IP packets.
- VLAN interface: Virtual interface that allows traffic from multiple VLANs to be handled by a single physical interface.
- Loopback interface: Used for routing purposes, not associated with physical interface.
- Tunnel interface: Used for VPNs, encapsulates packets for secure transmission over public networks.
Tunnel Zone
- Does not have any interface assigned to it, as it is used only for routing purposes between tunnel interfaces in Layer 3 zones.
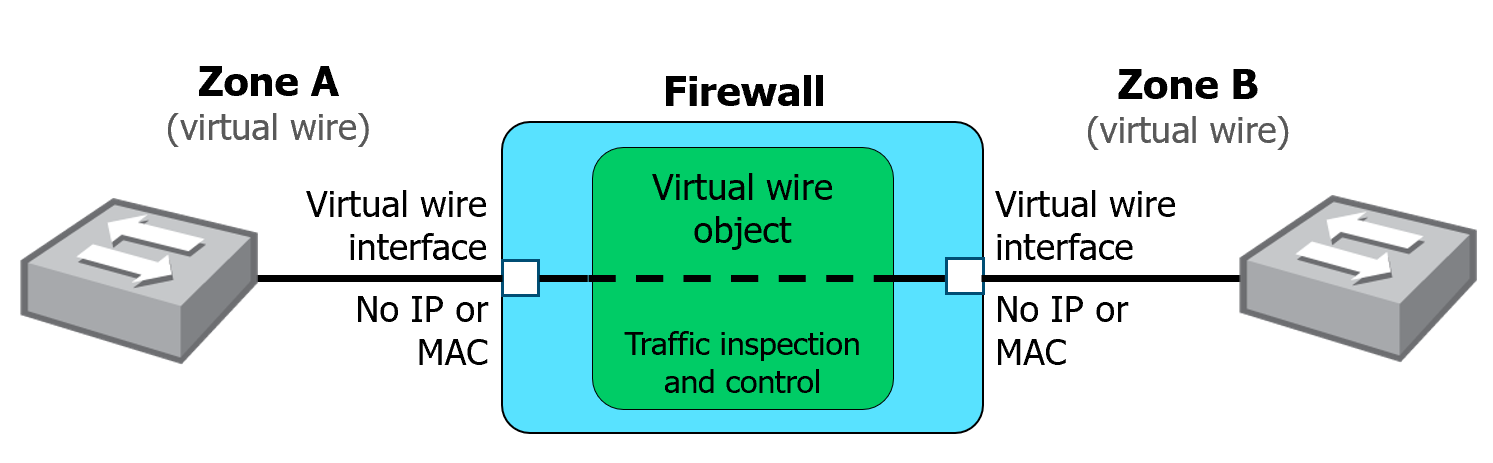
Virtual Wire Zone
- Virtual Wire interface: Transparently forwards traffic between two interfaces without applying security policies.
A zone cannot contain interfaces of different types, e.g., a Layer 2 zone cannot contain a Layer 3 interface.
Virtual Routers
- Virtual Router
- Logical router that allows traffic to flow between different networks.
- Supports one or more static routes.
- Default Route: Route that specifies the next hop for all traffic not defined in the routing table.
- Multiple default routes can be configured, and route with lowest metric is used.
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.