[EH Wk 1] Module 01: Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Ethical Hacking
- Process of testing and validating security measures of an organisation’s information systems and provide remediation strategies.
- Includes using tools and techniques used by threat actors to spot vulnerabilities in systems without the bounds of legality.
Classification of Attacks
Passive Attacks
- Does not tamper with data
- Generally conducted through intercepting information like network traffic
- Includes sniffing and eavesdropping
Active Attacks
- Will tamper with data.
- Can disrupt communication or services between systems.
- Includes DoS, Man-in-the-middle.
Close-in Attacks
- Conducted by attackers that are in close physical proximity to target system.
- Can be both passive, and active attack.
- Includes social engineering, eavesdropping, dumpster diving.
Insider Attacks
- Conducted by trusted users within a network.
- Use privileged access to violate rules to cause a threat to organisation’s information or system.
- Includes theft of physical devices, planting keyloggers, backdoors and malware.
Distribution Attacks
- Hardware or software attacks that are tampered with prior to distribution/installation.
- Could occur at source or transit
- Includes supply chain attacks
Methodologies / Frameworks / Models
CEH Hacking Methodology (CHM)
- Footprinting
- Scanning
- Enumeration
- Vulnerability Analysis
- System Hacking
- Gaining Access
- Escalating Privileges
- Maintaining Access
- Clearing Logs
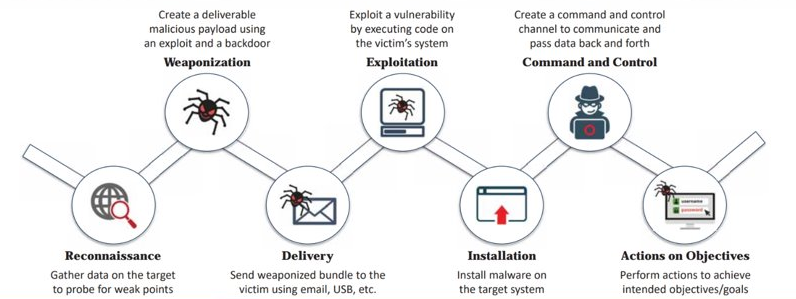
Cyber Kill Chain Methodology
- The sequence of steps an attacker takes to infiltrate a target system
- Component of intelligence-driven defense strategy to detect and prevent malicious intrusion activities
- Important to understand adversary’s tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) beforehand
- Reconnaissance
- Weaponization
- Delivery
- Exploitation
- Installation
- Command and Control (C2)
- Actions on Objectives
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
- Tactics:
- Guidelines on the way(s) an attacker conducts an attack
- Tactics exist for different stages of an attack (e.g. initial exploitation, privilege escalation, lateral movement, etc.)
- Techniques:
- Technical methods employed by an attacker
- Includes initial exploitation, setting up C2 servers, and accessing target infrastructure.
- Procedures:
- Organisational approach that threat actors follow
MITRE ATT&CK Framework
- Reconnaissance
- Weaponize
- Deliver
- Exploit
- Control
- Execute
- Maintain
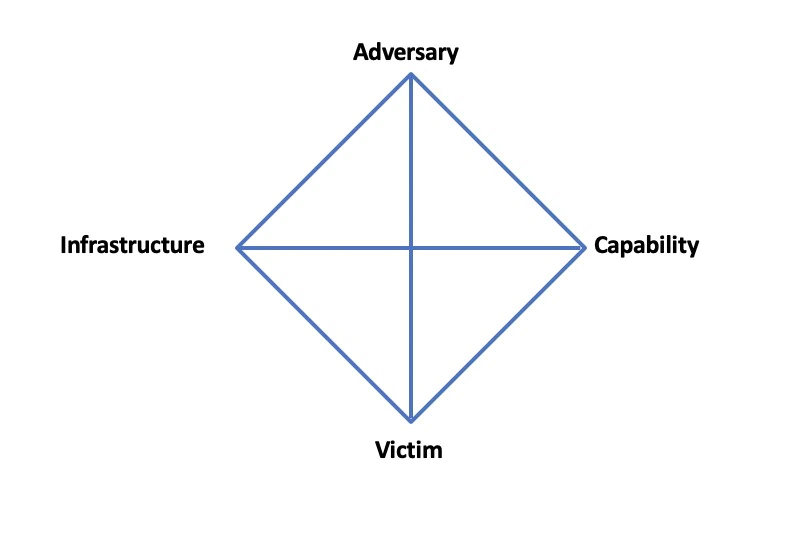
Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis
 Ref: Trellix
Ref: Trellix
- Used to identify clusters of events that are correlated to any system intrusion
- Adversary: Entity who was behind an attack
- Victim: Location where exploitation occurred or target that was attacked
- Capability: How the attack was performed or strategies used, e.g. skills
- Infrastructure: What was used to perform the attack, e.g. C2 servers, malware, etc.
Types of Hackers
- Black Hat: Illegal, unethical hacking
- White Hat: Legal hackers, using skills for defensive purposes
- Grey Hat: Works both offensively and defensively
- Cyberterrorists: Hackers that cause fear through disruptions or damage to systems
- Hacktivists: Hackers that use hacking to promote political agendas
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.