[NS Wk 6] Content Identification
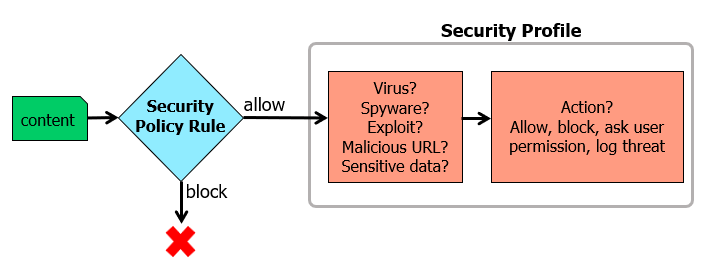
Security Profile Overview
Content-ID
- Threat prevention engine and policies to inspect and control data flowing through the firewall
- Typically scans for:
- Software vulnerability exploits
- Viruses
- Spyware
- Malicious URLs
- Restricted Files and Data
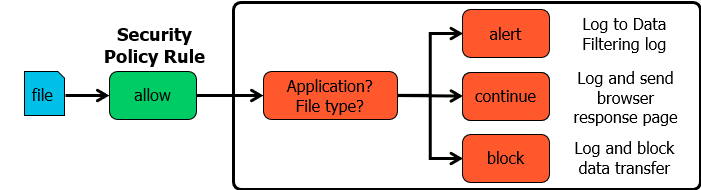
Security Policy with Security Profiles
- Basically second layer of defence for traffic that may slip through security policy rules
Security profiles only apply to security policy rules that are configured with the “Allow” action.
Security Profile Types
- Antivirus: Detects infected files being transferred with the application
- Anti-Spyware: Detects spyware downloads and traffic from already installed spyware
- Vulnerability Protection: Detects attempts to exploit known software vulnerabilities
- URL Filtering: Classifies and controls web browsing based on content
- File Blocking: Tracks and blocks file uploads and downloads based on file type and application (Sussy zip/exe files from sussy sites )
- Data Filtering: Identifies and blocks transfer of specific data patterns found in network traffic (Could be used to secure sensite data like credit card information)
- WildFire Analysis: Forwards unknown files to the WildFire service for malware analysis
Antivirus, Anti-Spyware, and Vulnerability Profiles
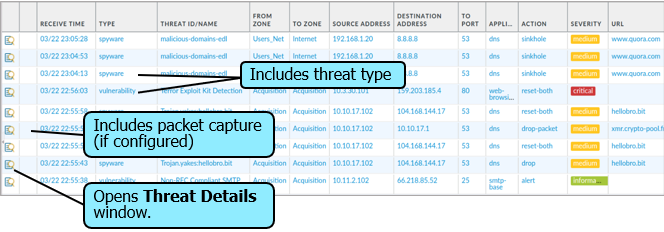
- Threat Log
Monitor > Logs > Threat
- Additional columns of information can be displayed/ removed.
- Some potentially useful additional column headers include the “ID column” that possesses ID numbers, that can used to create threat exceptions in firewall rules
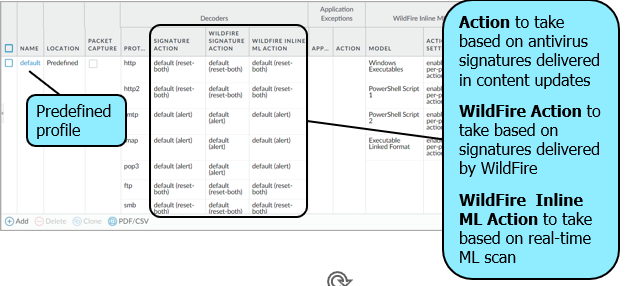
Antivirus Security Profiles
Default Antivirus Security Profiles
Objects Security Profiles > Antivirus
- Protects against viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware installations
- Malware prevention engine that analyses packets as they arrive, using a stream-based approach
- Default action varies based on protocol, such as reset-both for FTP, HTTP, and SMB.
- Default anti-virus security profile is Read Only (Cannot be deleted or modified )
- Actions include:
- Alert: Allows traffic to pass, but entry will be created in threat log
- Reset-both: Resets TCP server and client or drops UDP packets
Creating a New Antivirus Profile
Objects Security Profiles > Antivirus > Add
- Actions can be modified from default settings
- allow: Permits the traffic without logging
- alert: Permits and logs the traffic
- drop: Discards the traffic and generates a log entry
- reset-client: For TCP, resets the client-side connection. For UDP, drops the connection.
- reset-server: For TCP, resets the server-side connection. For UDP, drops the connection.
- reset-both: For TCP, resets the connection on both the client and server. For UDP, drops the connection.
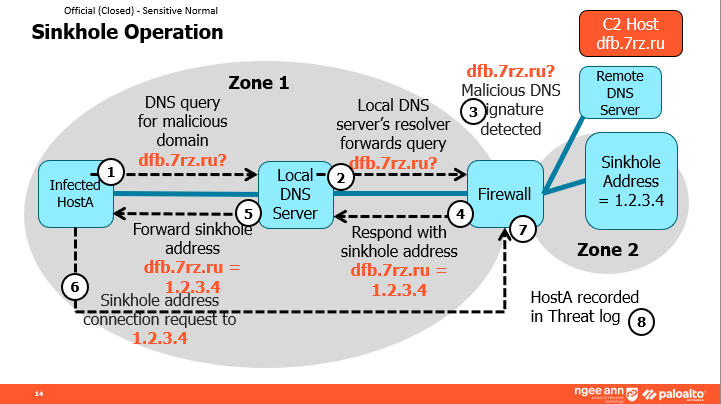
Sinkhole Operation
- Quickly identifies infected hosts within a network
- The firewall forges responses to the DNS queries, so clients try to connect to the specified sinkhole IP address rather than to a known malicious domain name.
- Sinkholes could often be utilized to analyse the malicious traffic
- Sinkholes do not have to be assigned to a real host, but it should be located in a different zone from the DNS client. (Traffic is only logged during interzone transmission by default)
Vulnerability Protection Profiles
- default: This profile applies the “default” action to all client and server critical, high-severity, and medium-severity events. The default profile typically is used for proof-of-concept or first-phase deployments.
- strict: This profile applies the “reset-both” response to all client and server critical, high-severity, and medium-severity spyware events and uses the “default” action for all client and server informational and low events. The strict profile is used for out-of-the-box protection with a recommended block of critical, high-severity, and medium-severity threats.
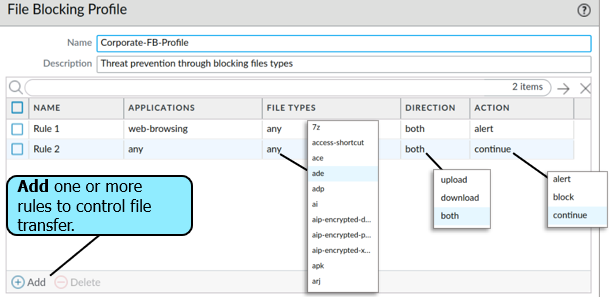
File Blocking Profiles
File Blocking Overview
- Prevent introduction of malicious data
- Prevent sensitive data from being breached
- Information is logged to Data Filtering Log
Creating a New File Blocking profile
Objects > Security Profiles > File Blocking > Add
- “Continue” actions require user permission to complete the file transfer.
- A page will pop up when paired with the application “web-browing”
Blocking Multi-Level Encoded Files
- Files can be encoded my mutliple layers of protocols and aopplications (A .docx file may contain XML and binaries, potentially further encoded if zipped)
- PAN-OS decodes up to four layers
- Files encoded more than four layers cannot be fully decoded but can be blocked by a File Blocking Profile.
Data Filtering Profiles
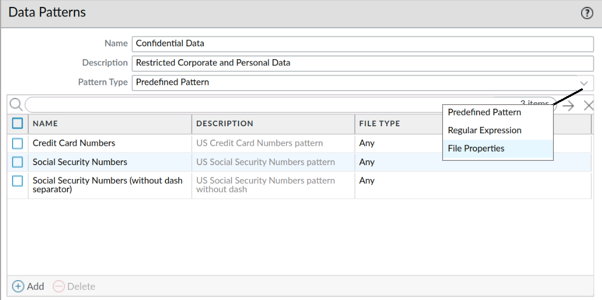
Creating a Data Pattern
Objects > Custom Objects > Data Patterns > Add
- Filter on key words, such as a sensitive project name or the word “confidential”
- Three types of data patterns for the firewall to use when scanning for sensitive information:
- Predefined Pattern: Use the predefined data patterns to scan files for Social Security and credit card numbers
- Regular Expression: Create custom data patterns using regular expressions
- File Properties: Scans files for specific file properties and values
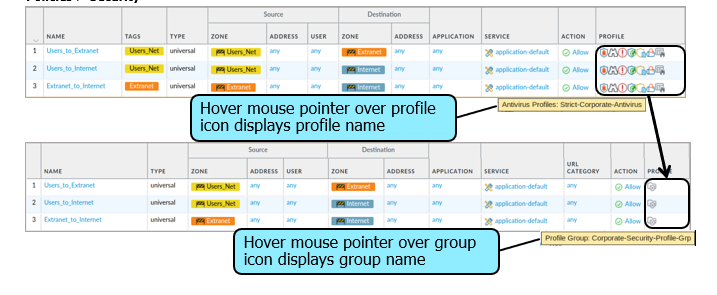
Attaching Security Profiles to Security Profile Rules
Assigning Security Profiles to Security Rules
- Assign individual Security Profiles to a Security policy rule
- Assign a Security Profile Group to a Security policy rule
Security Policy
-
Security Policy Rules:
- Enable control of traffic by allowing or blocking it on the network.
-
Security Profiles:
- Define “allow but scan” rules to scan allowed applications for threats like viruses, malware, spyware, and DDOS attacks. Applied when traffic matches the allow rule in the security policy, enabling further content inspection such as antivirus checks and data filtering.
-
Security Profile Groups:
- Combine commonly applied security profiles. Can be added to security policies as a unit, simplifying configuration. Optionally set up a default security profile group to include in policies by default.
Policies > Security
URL Filtering Security Profiles
Challenges with Preventing Web-Based Threats
- Enable business without compromising security
- Encrypted web content
- Silo management ( Managing different departments or teams in an organization that work separately, without sharing information or collaborating)
URL Filtering Profiles
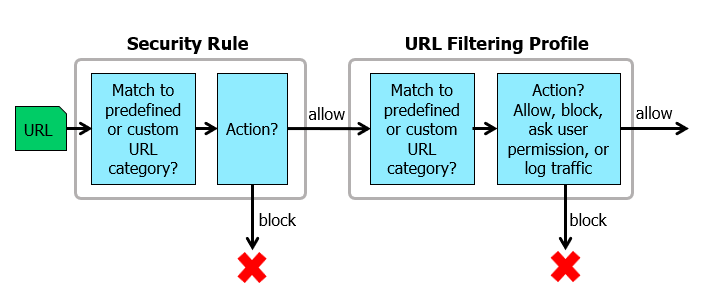
- Similar to security profiles, where URL filtering acts as a second layer of defence, for policy rules that are configured with an action of “Allow”.
URL Category: Policy Versus Profile
| URL Category in a Policy | URL Filtering Security Profile |
|---|---|
| Used as a match condition | Applied to traffic allowed by Security policy |
| URLs matched to predefined or custom URL categories | URLs matched to predefined or custom URL categories |
| Action determined in the policy rule | Action more granularly configured for individual URLs or URL categories |
| URL category name logged in the URL Filtering log | URL details logged in the URL Filtering log |
URL Filtering Security Profile
- The Palo Alto Networks firewall includes a predefined default URL Filtering Profile, which is read-only
- The default profile blocks websites like known malware, phishing, and adult content sites.
- Default profile cannot be modified or deleted; customize by cloning and editing or creating new profiles.
URL Filtering Security Default Categories
-
PAN-DB Classification:
- Websites classified based on content, features, and safety by PAN-DB. URLs categorized with up to four categories, including risk levels (high, medium, low) indicating threat exposure likelihood.
-
Security-Focused URL Categories:
- Aid in reducing attack surface by enabling targeted decryption and enforcement for sites with varying risk levels. Policy enforcement dynamically adapts as site content changes; no change requests allowed for security-focused categories.
-
Malicious URL Categories:
- Identify URLs with malicious or exploitive content, including malware, phishing, and command-and-control categories. Default URL Filtering profile blocks categories like abused-drugs, adult, gambling, hacking, questionable, and weapons.
-
Verified URL Categories:
- Contain URLs verified by Palo Alto Networks, without an associated risk level. Risk levels applicable only to unverified URLs. Some verified categories are considered malicious and blocked by default due to high risk.
Available actions for URL Filtering
- alert: Allows the user to access the website but adds an alert to the URL Filtering log
- allow: Allows the user to access the website; no log or user message is generated.
- block: Traffic is blocked, a block log entry is added to the URL Filtering log, and a response page is sent to the user’s browser.
- continue: A response page is sent to the user’s browser that prompts the user to click Continue to proceed and logs the action to the URL - Filtering log. The “log” action is recorded as “block-continue” when the response page is generated and is changed to “continue” if the user clicks Continue.
- override: A response page is sent to the user’s browser that prompts the user for the administrator-defined override password and the firewall logs the action to the URL Filtering log.
- none: (for a custom URL category only) Allows the firewall to inherit the URL Filtering category assignment from the URL database vendor
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.