[NS Wk 4] Application Identification
App-ID Overview
- App-ID
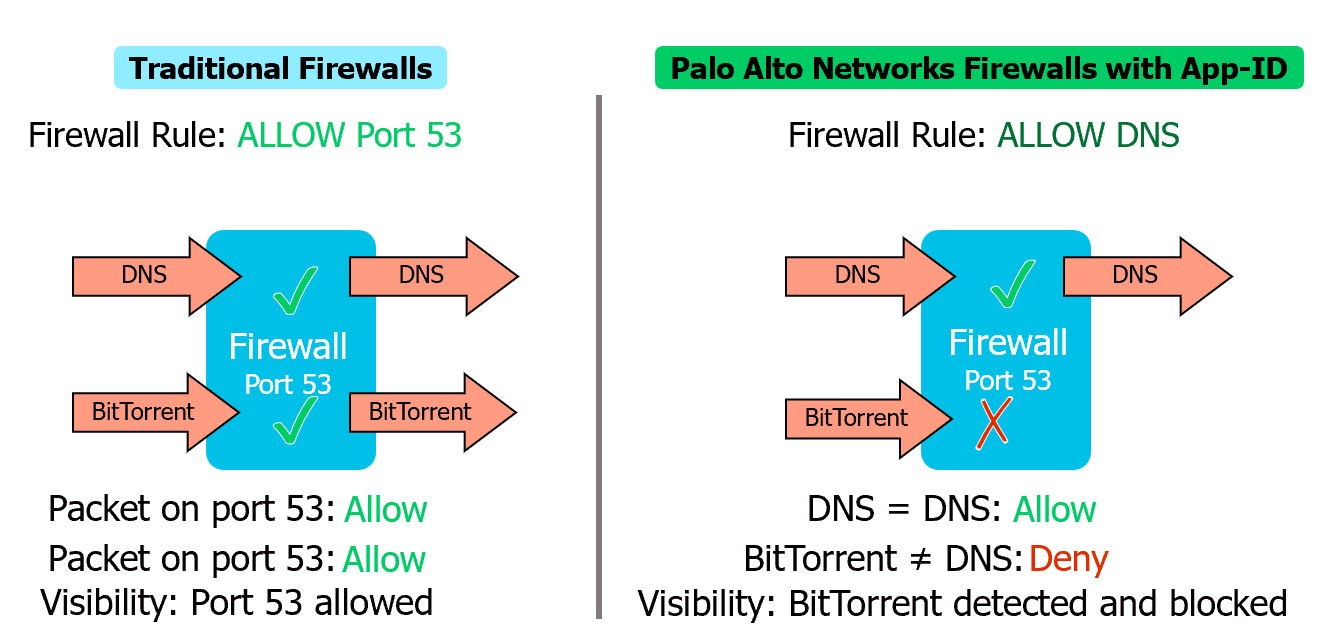
- Identifies applications in traffic and observed by firewall to understand their behaviour and set policies to control them.
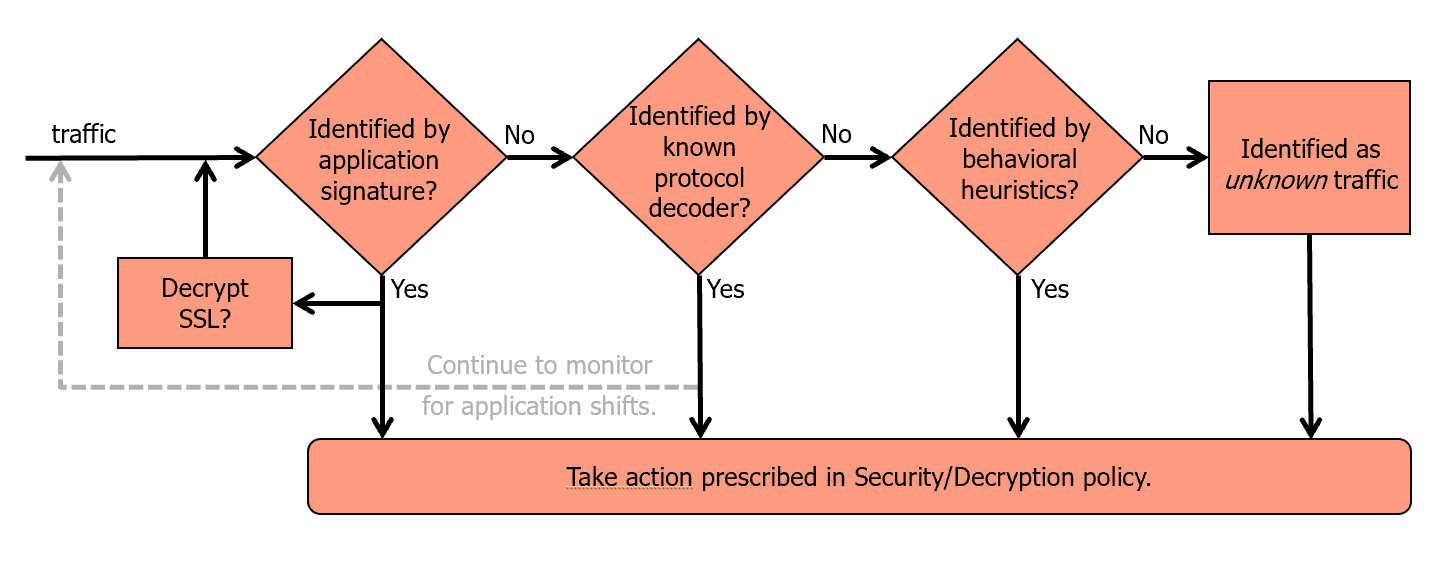
App-ID Process
- App-ID Signature Matching
- Identifies applications by matching traffic to application signatures.
- Signatures are based on application behaviour not port or protocol.
- Protocol Decoder Identification
- For protocols like SSL, SSH, check Decryption policy.
- Behavioural heuristics
- Attempts to identify behavioural patterns consistent with known applications.
- E.g.: Identifying BitTorrent traffic by identifying P2P traffic.
- Unknown Traffic
- Traffic not identified by App-ID and is handled by Security policy.
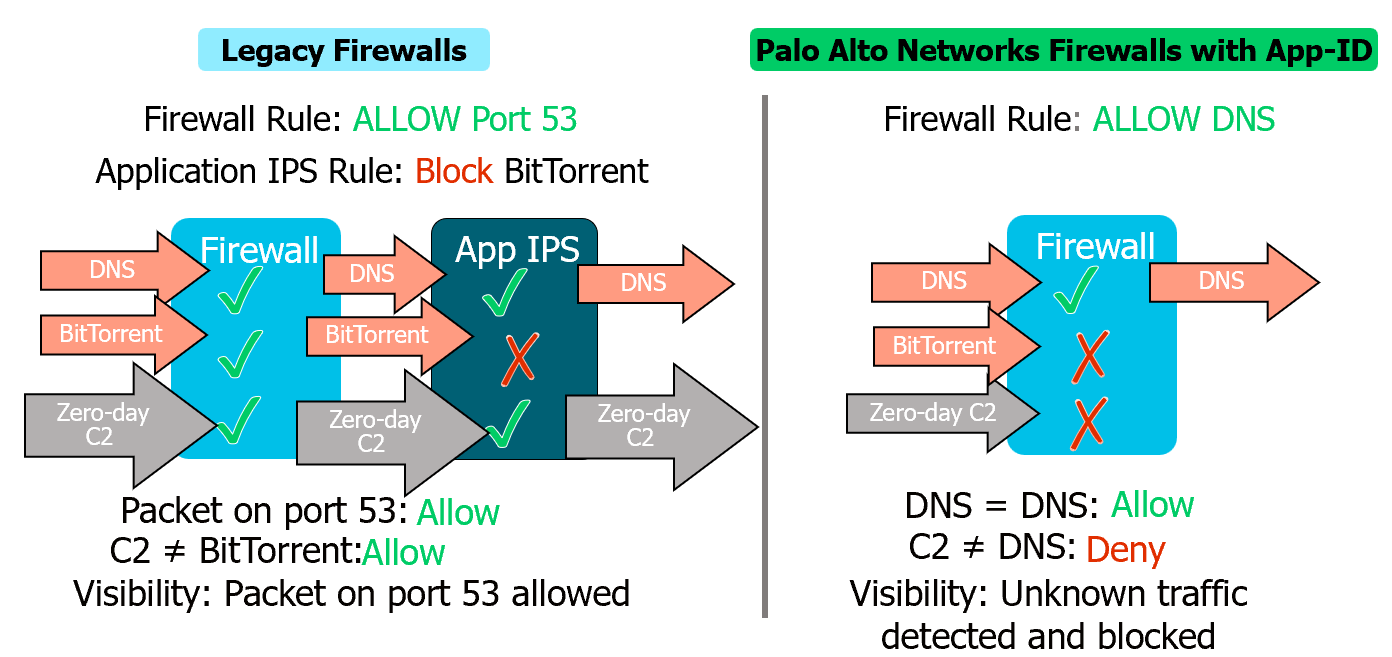
App-ID and Network Traffic
- Port-Based vs NGFW
- Zero-Day Malware Protection
App-ID and TCP
- In TCP, not all traffic contains application data (e.g.: SYN, ACK, FIN), so firewall must wait for the data to identify the application.
- App-ID labels TCP traffic using:
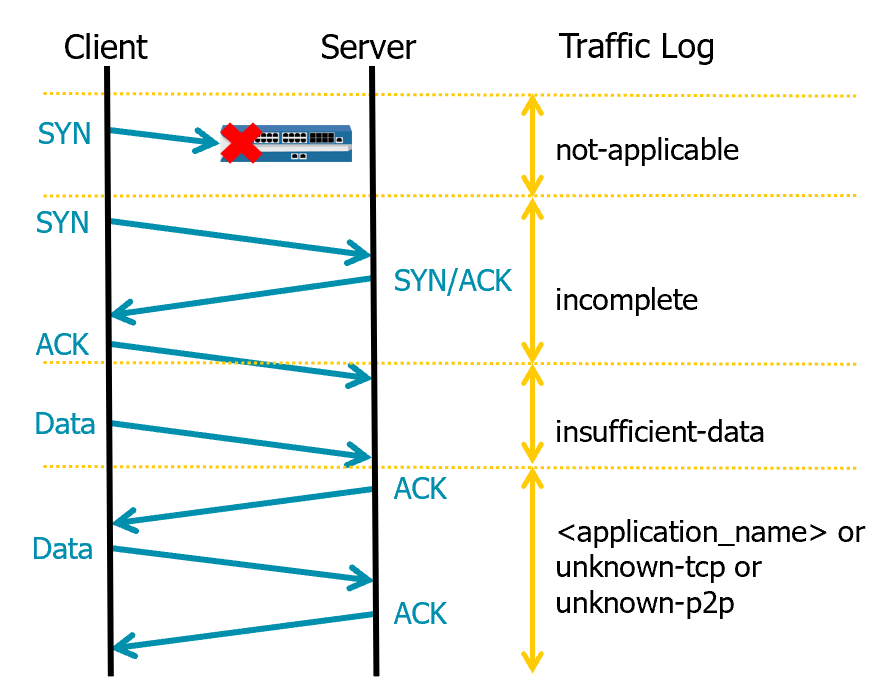
not-applicable: Traffic dropped per policy before application identification.incomplete: Three-way handshake did not complete or no data followed.insufficient-data: Not enough payload for identification.unknown-tcp: Unidentifiable TCP traffic.unknown-p2p: Unidentifiable peer-to-peer traffic.
App-ID and UDP
- In UDP, App-ID only examines a single UDP packet to identify the application.
- App-ID labels UDP traffic using:
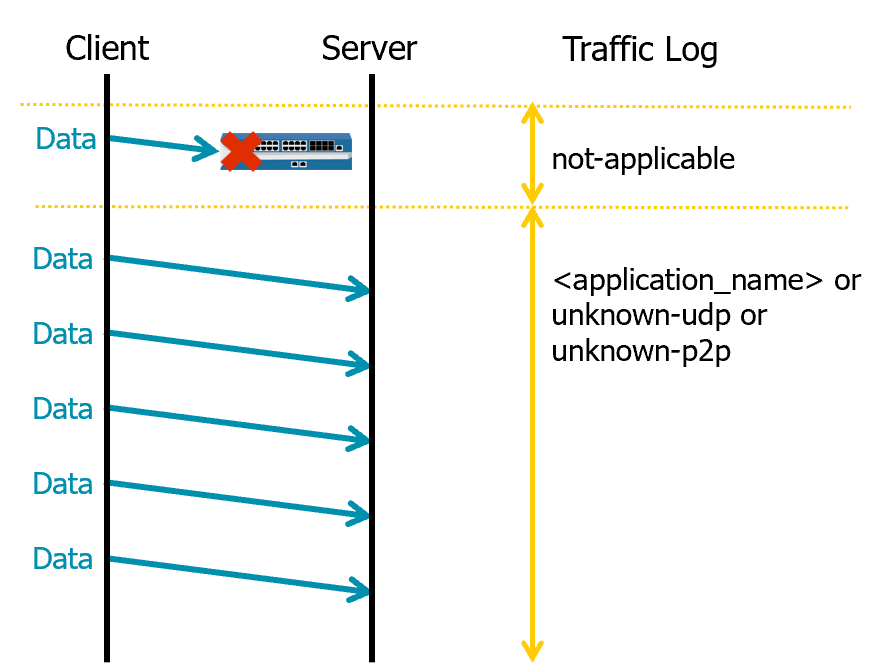
not-applicable: Traffic dropped per policy before application identification.unknown-udp: Unidentifiable UDP traffic.unknown-p2p: Unidentifiable peer-to-peer traffic.
App-ID Operations
Application Shifts
- Network traffic can shift from one application to another during a session. E.g.: web-browsing to facebook-chat.
- App-ID continuously monitors and updates the application label as more data is received.
Application Dependencies
- Some applications depend on other applications to function.
- Security policy must allow dependent applications for proper functioning.
Handling Unknown Traffic
Unknown Traffic Identification
- When App-ID cannot identify traffic, it is labelled as
unknown-tcp,unknown-udporunknown-p2p, if HTTP is not detected. - Security policy must be configured to handle unknown traffic.
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.